Rendering Pipeline
2024-09-06
最后编辑于:2024-09-15
Rendering Pipeline
VertexInput -> Vertex Assembly -> VertexOperation -> Primitive Assembly -> Rasterization -> FragmentOperation -> Depth Write
Look To
用于对世界空间中的顶点进行变换,以相机的视角向世界空间中一个方向旋转
Mat<4, 4, T> LookTo(const Vec3& eye, const Vec3& dir, const Vec3& up);
利用相对的思想,将相机移动到原点并构建坐标系,让世界相对相机旋转,再将相机移回原来的位置,最后求得这些变换的逆即可,这分为了平移和旋转两部分
先考虑旋转,根据线性代数基的变换,用一些相互正交的向量定义一个线性空间,并作为基向量构成一个矩阵,用这个矩阵相乘即可将向量变换到这个线性空间中.
我们可以利用这里的dir,up使用Gram-Schmidt Process来构建一个三维的坐标系,并用这三个轴作为基向量构建变换矩阵.
Vec3 F = Normalized(dir);
Vec3 R = Normalized(Cross(F, up));
Vec3 U = Normalized(Cross(R, F));
Mat<4, 4, T> {
R.x, U.x, -F.x, 0,
R.y, U.y, -F.y, 0,
R.z, U.z, -F.z, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1
}
注意,相机使用右手坐标系,但是对准的是-Z方向,这里需要反转F的方向来构建右手坐标系
平移就很简单了
Mat<4, 4, T> {
1, 0, 0, eye.x,
0, 1, 0, eye.y,
0, 0, 1, eye.z,
0, 0, 0, 1
}
最后对这两个变换求逆并合并 $M_{lookat}= M_{R}^{-1}M_{T}^{-1}$ 旋转矩阵的逆等于转置
Mat<4, 4, T> {
R.x, R.y, R.z, -Dot(R, eye),
U.x, U.y, U.z, -Dot(U, eye),
-F.x, -F.y, -F.z, -Dot(-F, eye),
0, 0, 0, 1
};
Perspective Projection
Eye space -> Projection transform -> Clip space -> Homogeneous division -> NDC
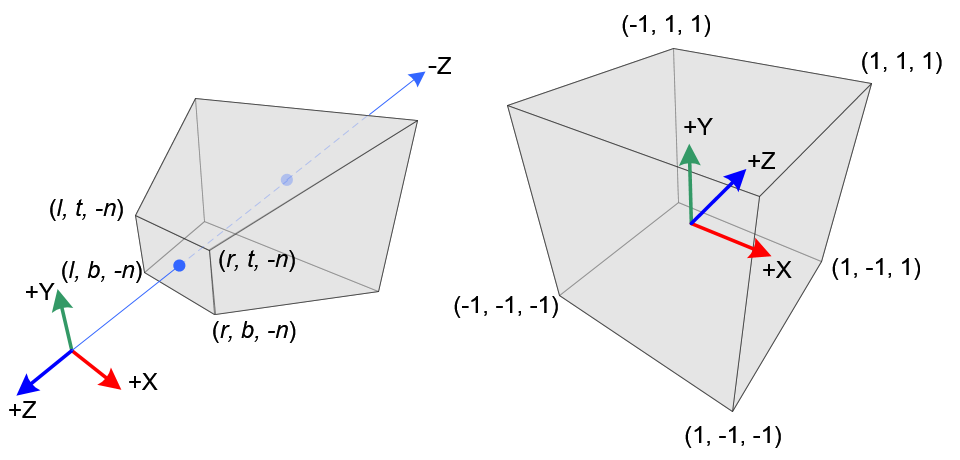
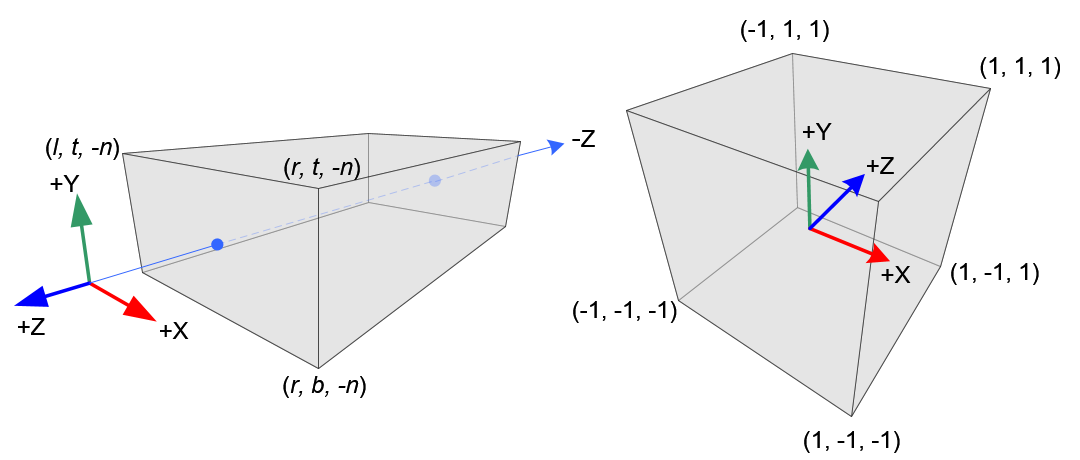
通过透视投影,将相机空间(Camera space or Eye Space)变换到裁剪空间(Clip space),在视锥剔除(Frustum Culling)后,进行齐次除法(Homogeneous Division),就变换到了NDC空间(Normalized Device Coordinates or Canonical View Volume),可以理解为将视锥压缩为一个标准立方体 注意相机空间使用的是右手系,在NDC空间中则是左手系
先考虑X,Y方向,利用三角形相似得到投影在近平面上的坐标
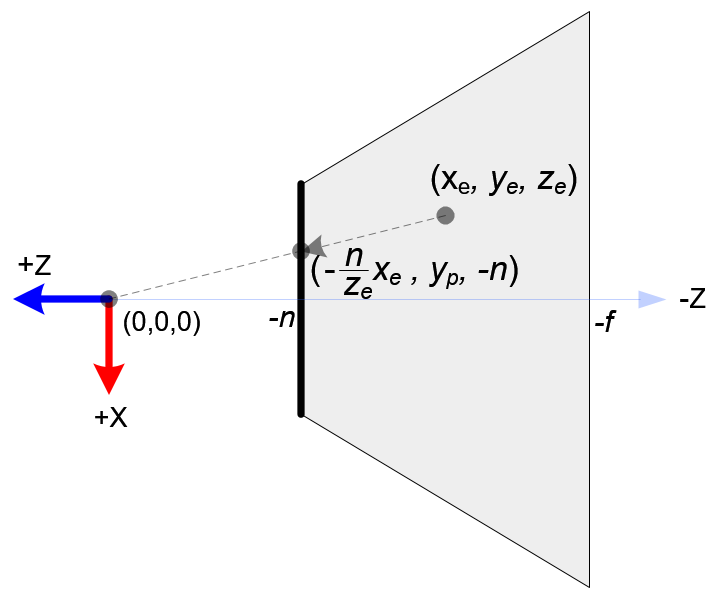
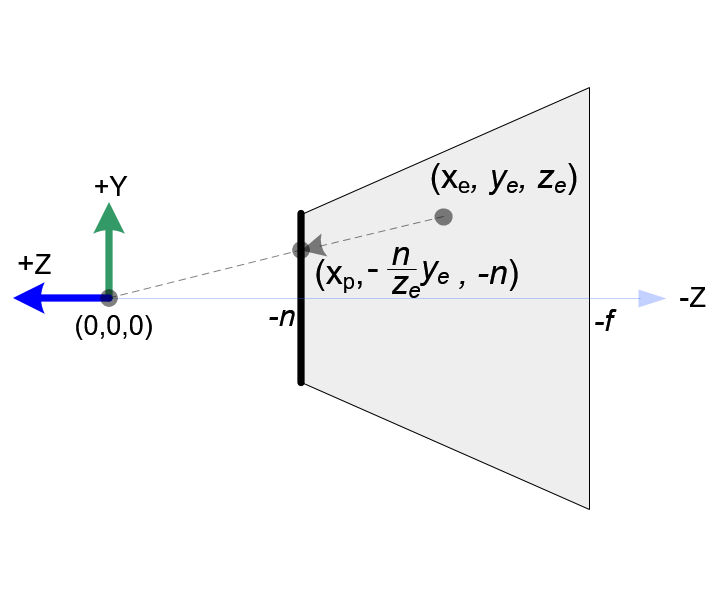
$$ \begin{align} x_p=-\frac{n}{z_e}x_e\ y_p=-\frac{n}{z_e}y_e \end{align} $$
可以发现 $x_p$ 和 $y_p$ 都与 $-z_e$ 成反比
接下来是将近平面上点的坐标映射到 $[-1,1]^2$ ,即映射到NDC空间
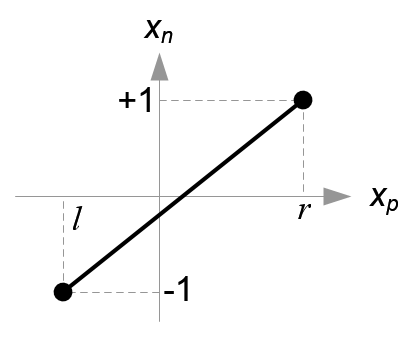
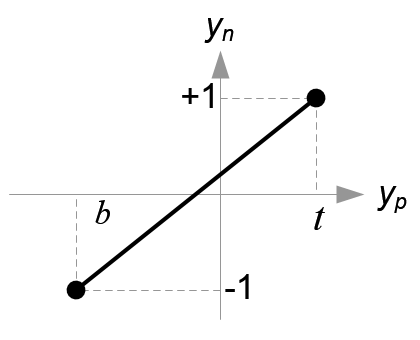
$$ \begin{align} x_n=\frac{2}{r-l}x_p-\frac{r+l}{r-l}\ y_n=\frac{2}{t-b}y_p-\frac{t+b}{t-b} \end{align} $$
代入投影坐标可以得到
$$ x_n=\frac{2nx_e}{r-l}/(-z_e)-\frac{r+l}{r-l}=(\frac{2nx_e}{r-l}+\frac{r+l}{r-l}z_e)/(-z_e) $$
$$ y_n=\frac{2ny_e}{t-b}/(-z_e)-\frac{t+b}{t-b}=(\frac{2ny_e}{t-b}+\frac{t+b}{t-b}z_e)/(-z_e) $$
注意这里已经是齐次除法之后的坐标了,我们需要利用其特性来反推透视矩阵是如何将相机空间变换到裁剪空间的
$$ V_{clip}=M_{PerspProj}V_e=\begin{bmatrix} a&b&c&d\ e&f&g&h\ i&j&k&l\ m&n&o&p \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}{x_e}\ \color{green}{y_e}\ \color{blue}{z_e}\ w_e \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} a\textcolor{red}{x_e}+b\textcolor{green}{y_e}+c\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+dw_e\ e\textcolor{red}{x_e}+f\textcolor{green}{y_e}+g\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+hw_e\ i\textcolor{red}{x_e}+j\textcolor{green}{y_e}+k\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+lw_e\ m\textcolor{red}{x_e}+n\textcolor{green}{y_e}+o\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+pw_e\ \end{bmatrix} $$
齐次除法后
$$ V_n=V_{clip}/w_{clip}=\begin{bmatrix} x_{clip}/w_{clip}\ y_{clip}/w_{clip}\ z_{clip}/w_{clip}\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
依据上文推导的关系式,可以初步化简与z分量无关的部分,其中相机空间中 $w_e=1$
$$ V_{clip}=\begin{bmatrix} a&0&c&0\ 0&f&g&0\ 0&0&k&l\ 0&0&o&p \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}{x_e}\ \color{green}{y_e}\ \color{blue}{z_e}\ w_e \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} a\textcolor{red}{x_e}+c\textcolor{blue}{z_e}\ f\textcolor{green}{y_e}+g\textcolor{blue}{z_e}\ k\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+l\ o\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+p\ \end{bmatrix} $$
到这一步可以观察到 $a\textcolor{red}{x_e}+c\textcolor{blue}{z_e}$ 与 $x_n$ 的形式很接近了,只相差一个被除数 $-z_e$ ,而在齐次除法中正是要除以 $w_{clip}$ ,所以将 $w_{clip}$ 设为$-z_e$ 借助这个关系还可以将第四行也全部确定
$$ V_{clip}=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{2n}{r-l}&0&\frac{r+l}{r-l}&0\ 0&\frac{2n}{t-b}&\frac{t+b}{t-b}&0\ 0&0&k&l\ 0&0&-1&0 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}{x_e}\ \color{green}{y_e}\ \color{blue}{z_e}\ w_e \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} a\textcolor{red}{x_e}+c\textcolor{blue}{z_e}\ f\textcolor{green}{y_e}+g\textcolor{blue}{z_e}\ k\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+l\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
现在来单独解决第三行
$$ z_n=\frac{z_{clip}}{w_c}=\frac{kz_e+lw_e}{-z_e}=-k-\frac{l}{z_e} $$
使用近平面中心(0, 0, -n, 1)和远平面中(0, 0, -f, 1)两个与x,y无关的特殊点构造方程组来求解
$$ \begin{align} -1=-k-\frac{l}{-n}\ 1=-k-\frac{l}{-f} \end{align} $$
解得
$$ \begin{align} k=\frac{n+f}{n-f}\ l=\frac{2nf}{n-f} \end{align} $$
最终得到
$$ M_{PerpProj} \begin{bmatrix} \frac{2n}{r-l}&0&\frac{r+l}{r-l}&0\ 0&\frac{2n}{t-b}&\frac{t+b}{t-b}&0\ 0&0&\frac{n+f}{n-f}&\frac{2nf}{n-f}\ 0&0&-1&0 \end{bmatrix} $$
如果使用Vertical field of view, Aspect ratio和near, far来定义 首先有
$$ \begin{align} r+l=0\ t+b=0\ \frac{t}{n}=tan\frac{\theta}{2}\ \frac{r}{t}=aspect \end{align} $$
化简后
$$ M_{PerpProj} \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{tan\frac{\theta}{2}aspect}&0&0&0\ 0&\frac{1}{tan\frac{\theta}{2}}&0&0\ 0&0&\frac{n+f}{n-f}&\frac{2nf}{n-f}\ 0&0&-1&0 \end{bmatrix} $$
Orthographic Projection
正交投影并不会产生齐次坐标,所以 $V_n=V_c$ , $w_e=w_c=1$
$$ V_{clip}=M_{OrthoProj}V_e \begin{bmatrix} a&b&c&d\ e&f&g&h\ i&j&k&l\ m&n&o&p \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}{x_e}\ \color{green}{y_e}\ \color{blue}{z_e}\ 1 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} a\textcolor{red}{x_e}+b\textcolor{green}{y_e}+c\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+d\ e\textcolor{red}{x_e}+f\textcolor{green}{y_e}+g\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+h\ i\textcolor{red}{x_e}+j\textcolor{green}{y_e}+k\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+l\ m\textcolor{red}{x_e}+n\textcolor{green}{y_e}+o\textcolor{blue}{z_e}+p\ \end{bmatrix} $$
直接由相机空间向NDC空间的映射着手
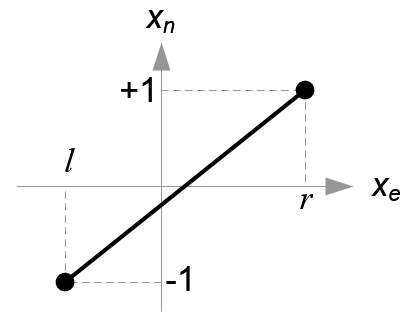
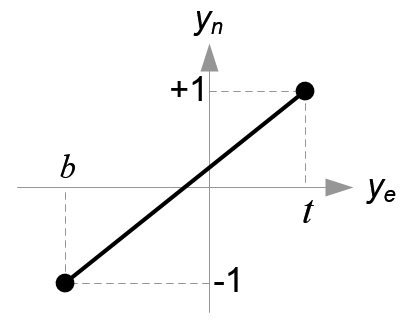
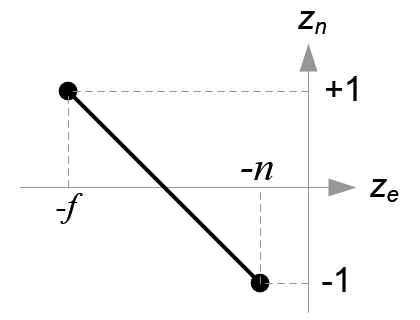
$$ x_n=\frac{2}{r-l}x_e-\frac{r+l}{r-l} $$
$$ y_n=\frac{2}{t-b}y_e-\frac{t+b}{t-b} $$
$$ z_n=-\frac{2}{f-n}y_e-\frac{f+n}{f-n} $$
得到
$$ M_{OrthoProj}=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{2}{r-l}&0&0&-\frac{r+l}{r-l}\ 0&\frac{2}{t-b}&0&-\frac{t+b}{t-b}\ 0&0&\frac{2}{f-n}&-\frac{f+n}{f-n}\ 0&0&0&1 \end{bmatrix} $$
若坐标是对称的,可以化为更简单的形式
$$ M_{OrthoProj}=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{r}&0&0&0\ 0&\frac{1}{t}&0&0\ 0&0&\frac{2}{f-n}&-\frac{f+n}{f-n}\ 0&0&0&1 \end{bmatrix} $$